GoF 的 Design Patterns [1] 一書在 Visitor pattern 的實做描述中提到了 single/double dispatch,並針對 single dispatch 給了這樣的說明:
In single-dispatch languages, two criteria determine which operation will fulfill a request: the name of the request and the type of receiver
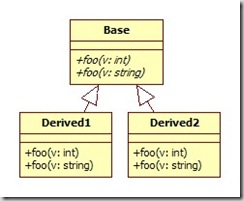
若要快速地瞭解這句話,我們不妨白話點:函式的喚起是倚賴 function overriding (dynamic polymorphism) 與 overloading (static polymorphism) 的合作而完成的。以 C++ 為例,假設我們有以下的繼承架構:
當我們寫下這段程式碼時:
Base* ptr = new Derived1; ptr->foo( 1 );會被喚起的函式是 Derived1::foo( int ),而非 Base::foo( int ) ,當然更不可能是 Derived2::foo( int ),這是 function overriding (dynamic polymorphism),以 C++ 說,因為當下物件 ptr 的 vtbl 指向的型別是 Derived1 而非 Base ,這也就是 GoF 書中提到的 type of receiver 的部份。至於為何是 Derived1::foo( int ) 而不是 Derived1::foo( string ),就是倚賴 function overloading ,相當於GoF 書中提到的 name of the request 。
那什麼是 double dispatch 呢?耶,有 double ,那有沒有 triple 呢?quadruple 呢?…?答案是有,而且我們還習慣把它們合在一稱為 multiple dispatch ,在另一本 OO 聖經書籍 Generative Programming [2] 中提到:多型機制可分為兩大類:single dispatch 和 multiple dispatch (又稱 multimethods):
Single dispatch corresponds to the Smalltalk idea of sending a message to an object, where the appropriate method (i.e., message implementation) is selected based on the type of the reciever.
…
Single dispatch introduces asymmetry with respect to the arguments because the first argument is treated specially.
…
A dispatch mechanism that uniformly uses all argument types for selecting the method is referred to as multiple dispatch, or mutlimethods.
從上面的解釋中我們不難體會:常見語言(如:C++, Java, C# )的動態多型呼叫是可轉換成對等的 C 語言,轉換的虛擬碼如:
// C++
Base* ptr = new Derived1;
ptr->foo( 1 );
// C
foo_in_c( ptr, 1 );
foo_in_c( Base* ptr, int i )
{
if ( "Base" == ptr->type_info() )
Base::foo_in_c( i );
else if ( "Derived1" == ptr->type_info() )
Derived1::foo_in_c( i );
else
Derived2::foo_in_c( i );
}
我們可以透過 this 得到 ptr 的記憶體位置,並傳給轉換後的 foo_in_c 去決定該喚起的是哪個 method ,這種將第一個參數特別挑出來檢驗的機制就稱作 single dispatch ,反之,若是今天 foo 有 N 個參數,函式的喚起得考慮 run-time 時,每個參數的實際型別,那就是 multiple dispatch 。
Multiple dispatch 比起 single dispatch 更具有表達與描述威力,因為同一個時間點,它同時考慮了多個 物件的 run-time 型別。而目前只有少數語言有支援這個特色:如 CLOS 。其他語言則需要透過 extension 。[7] 羅列了一些這類的整理資料,
針對 C++ ,除了找 extension 外,還可以在經典書籍 Modern C++ Design 的第十一章,看到 Andrei 的一些討論。另外,[9] 這篇 C++ Report 的文章也提出了一個解法,[10] 則針對上面兩個方法有所簡單討論, [9] 也是從這找到的。
Reference
- Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented Software by Erich Gamma, Richard Helm, Ralph Johnson, 1998
- Generative Programming: Methods, Tools, and Applications by Krzysztof Czarnecki and Ulrich W. Eisenecker, Addison Wesley, 2000
- Generative Programming: http://www.generative-programming.org/
- Modern C++ Design: Generic Programming and Design Patterns Applied by Andrei Alexandrescu, Addison Wesley, 2001
- Dynamic Dispatch - wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_dispatch
- Double Dispatch - wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Double_dispatch
- Multiple Dispatch - wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiple_dispatch
- Single, Double and Multiple Dispatch: http://ifacethoughts.net/2006/07/29/single-double-and-multiple-dispatch/
- Multiple Dispatch A New Approach using templates and RTTI: http://www.eptacom.net/pubblicazioni/pub_eng/mdisp.html
- Re: 備份 : Multiple Dispatch: http://phpbb.godfat.org/viewtopic.php?t=204&highlight=&sid=0ffb75220260fea3aa497c8a17fe710b





沒有留言:
張貼留言